Most employers need an LMIA before they can hire a temporary foreign worker. Before you start the hiring process, you must determine if you need an LMIA.
LMIA is a legal document assessing the potential impact if employers are hiring foreign workers. This exists to make sure that jobs in Canada must be available to Canada citizens or permanent residents first. Employers, in most circumstances, can only hire an international worker/ employee if they have a positive LMIA confirming that:
- there is a need for a temporary foreign worker.
- no Canadians or permanent residents are available to do the job.
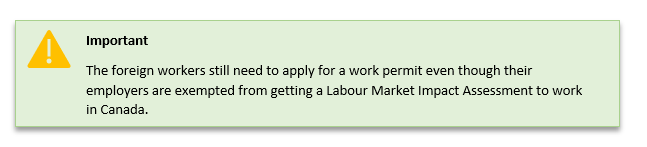
However, there are several situations where an LMIA is exempt. If Canadian employer is exempted from obtaining an LMIA, they can hire a temporary foreign worker without first applying for an LMIA.
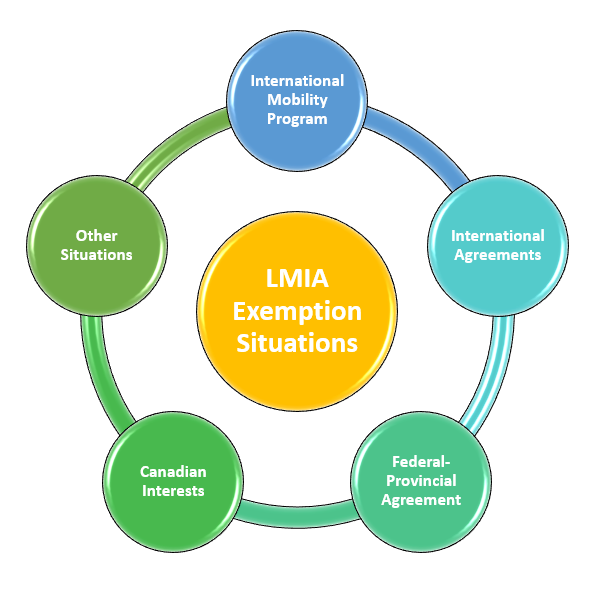
International Mobility Program
The International Mobility Program is designed to allow Canadian employers to hire temporary foreign workers without the need to obtain for a Labour Market Impact Assessment.
In most cases, to hire a temporary worker through the International Mobility Program, you must:
- pay the employer compliance fee of $230; and
- create and submit an offer of employment form through the Employer Portal. Your offer of employment must include information about:
- your business
- the foreign worker you would like to hire
- the job details
- wage and benefits
International Agreements
You may be exempt from needing an LMIA if your situation is covered by the international agreements between Canada and your country. There are several international agreements as below:
- North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
- Canada-Chile FTA / Canada-Peru FTA / Canada-Colombia FTA / Canada-Korea FTA
- Canada-European Union Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA)
- General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
Federal-Provincial Agreement
Under Canada’s Constitution, responsibility for immigration is shared between the federal and provincial/territorial governments.
The federal, provincial and territorial governments meet to plan and consult each other on immigration issues. In addition, Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) has agreements with provinces and territories on how they share responsibility for immigration.
Each agreement is negotiated separately with the province or territory to address unique needs and priorities. If the employer in located in the province which has an agreement in place with the federal government, it might be exempted from an LMIA to hire a foreign worker.
One example for this situation is if you are applying for a work permit under Atlantic Immigration Pilot Program, you are exempted from getting an LMIA due to the existence of an agreement between Atlantic and the Federal government.
Canadian Interests
Significant benefit – if your employer can prove you will bring an important social, cultural, and/or economic benefit to Canada. This can include:
- general: Self-employed engineers, technical workers, creative and performing artists, etc.
- workers transferred within a company (intra-company transferees with specialized knowledge) – only those that will benefit Canada with their skills and experience
- workers under Mobilité francophone
Reciprocal employment – lets foreign workers get jobs in Canada when Canadians have similar opportunities in other countries
- General (such as professional coaches and athletes working for Canadian teams)
- International Experience Canada – a work abroad program for youth and young professionals
- People in exchange programs like professors and visiting lecturers
Designated by the Minister
- Academics, including researchers, guest lecturers and visiting professors (sponsored through a recognized federal program)
- Competitiveness and public policy
- medical residents and fellows
- post-doctoral fellows and people who have won academic awards from Canadian schools
Charity and religious work (not including volunteers)
Other Situations
There are some other situations where an LMIA are exempt, as below
- Refugee
- Permanent residence applicants in Canada
- Vulnerable workers
- Humanitarian reasons
How to know if you are exempted from an LMIA
To see if you and the temporary foreign worker you want to hire are exempt from needing an LMIA or work permit, do one of the following:
- review the LMIA exemption codes and work permit exemptions (mentioned below)
- select the LMIA exemption or work permit code that seems most relevant to your hiring situation and read the detailed description.
- if an exemption code applies to you, you’ll need to include it in your offer of employment.
or
- contact the International Mobility Workers Unit (IMWU)
- available only if you’re hiring a temporary foreign worker who is both
- currently outside Canada
- from a country whose nationals are visa-exempt
- available only if you’re hiring a temporary foreign worker who is both
LMIA exemption codes
R204: International agreements
| R204(a) Canada-international exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| Non-trade
Unique work situations:
|
T11 |
| Trader (FTA) | T21 |
| Investor (FTA) | T22 |
| Professional/technician (FTA) | T23 |
| Intra-company transferee (FTA) | T24 |
| Spouse (Colombia or Korea FTA) | T25 |
| GATS professional | T33 |
| Investor (CETA) | T46 |
| Contractual service supplier (CETA) | T47 |
| Independent professional (CETA) | T43 |
| Intra-corporate (company) transferee (CETA) | T44 |
| Spouse (CETA) | T45 |
| Investor (CPTPP) | T50 |
| Intra-company transferee (CPTPP) | T51 |
| Professional or technician (CPTPP) | T52 |
| Spouse (CPTPP) | T53 |
R204(b) Provincial/territorial-international exemption codes
There are no approved agreements at this time
| R204(c) Canada-provincial/territorial exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| Canada-provincial/territorial | T13 |
| Atlantic Immigration Pilot Program | C18 |
R205: Canadian interests
| R205(a) Significant benefit exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| Significant benefit
Unique work situations:
|
C10 |
| Entrepreneurs
Unique work situations:
|
C11 |
| Intra-company transferees (including GATS)
Unique work situations
|
C12 |
| Emergency repair or repair personnel for out-of-warranty equipment | C13 |
| Television and film production workers | C14 |
| Francophone mobility | C16 |
| Live-in caregivers whose permanent residence application is submitted | A71 |
| Caregivers whose permanent residence application is submitted under the Home Child Care Provider Pilot (HCCPP) or Home Support Worker Pilot (HSWP) (occupation-restricted open work permit) | C90 |
| Spouses and dependants at age of majority of caregivers whose permanent residence application is submitted under the HCCPP or HSWP | C91 |
Bridging open work permits (BOWPs)
|
A75 |
Unique work situations
|
A75 |
| R205(b) Reciprocal employment exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| Reciprocal employment
Unique work situations:
|
C20 |
| Youth exchange programs | C21 |
| Academic exchanges (professors, visiting lecturers | C22 |
| Performing arts | C23 |
R205(c) Designated by Minister
| R205(c)(i) Research exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| Research | C31 |
| i.1) Educational co-op – post-secondary | C32 |
| i.2) Educational co-op – secondary level | C33 |
| R205(c)(ii) Competitiveness and public policy exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| Spouses of skilled workers | C41 |
| Spouses of students | C42 |
| Post-grad employment | C43 |
| Post-doctoral Ph.D. fellows and award recipients | C44 |
| Off-campus employment | See the instructions concerning students |
| Medical residents and fellows | C45 |
| R205(d) Charitable or religious work exemption code | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| Religious work | C50 |
| Charitable work | C50 |
R206: No other means of support
| R206 exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| a. Refugee claimants | S61 |
| b. Persons under an unenforceable removal order | S62 |
R207: Permanent residence applicants in Canada
| R207 exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
Permanent residence applicants in Canada:
|
A70 |
R207.1: Vulnerable workers
| R207.1 exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| 1. Vulnerable workers | A72 |
| 2. Family member of vulnerable worker | A72 |
R208: Humanitarian reasons
| R208 exemption codes | |
| Regulation | LMIA exemption code |
| a. Destitute students | H81 |
| b. Holders of a temporary resident permit valid for a minimum of six months | H82 |
Work permit exemption
Authorization to work without a work permit
- R186(a)—Business visitor
- R186(b)—Foreign representatives and R186(c)—Family members of foreign representatives
- R186(d)—Military personnel
- R186(e)—Foreign government officers
- R186(f)—On-campus employment
- R186(g)—Performing artists
- R186(h)—Athletes and team members
- R186(i)—News reporters, media crews
- R186(j)—Public speakers
- R186(k)—Convention organizers
- R186(l)—Religious leaders
- R186(m)—Judges, referees and similar officials
- R186(n)—Examiners and evaluators
- R186(o)—Expert witnesses or investigators
- R186(p)—Health care students
- R186(q)—Civil aviation inspector
- R186(r)—Aviation accident or incident inspector
- R186(s)—Crew
- R186(t)—Emergency service providers
- R186(u)—Implied status
- R186(v)—Off-campus work
- R186(w)—Off-campus work (transition to post-graduation status)
- R186(x)—Registered Indians
- Assessing farm work
- Public Policy: Short-term work permit exemption
- Public Policy: 120-day work permit exemption for researchers
Registered Indians
Registered Indians, as defined under the Indian Act, are exempt from having to apply for a work permit.



